语言是为满足群体协作的需要而产生的交流工具,也是人类区别于其它动物的重要标志之一。但是长期以来,大部分关于语言脑机制的研究都脱离了交流情境,将听和说割裂开来单独进行考察。因此,基于这些研究建立的语言加工认知神经机制模型可能并不适用于语言交流过程的阐释。
为此,卢春明课题组于2020年11月21日在《Social Cognitive and Affective Neurosciences》(SCAN)杂志发表了题为“A hierarchical model for interpersonal verbal communication” 的综述文章,提出了适用于人际间言语交流的认知神经层级模型(图1)。
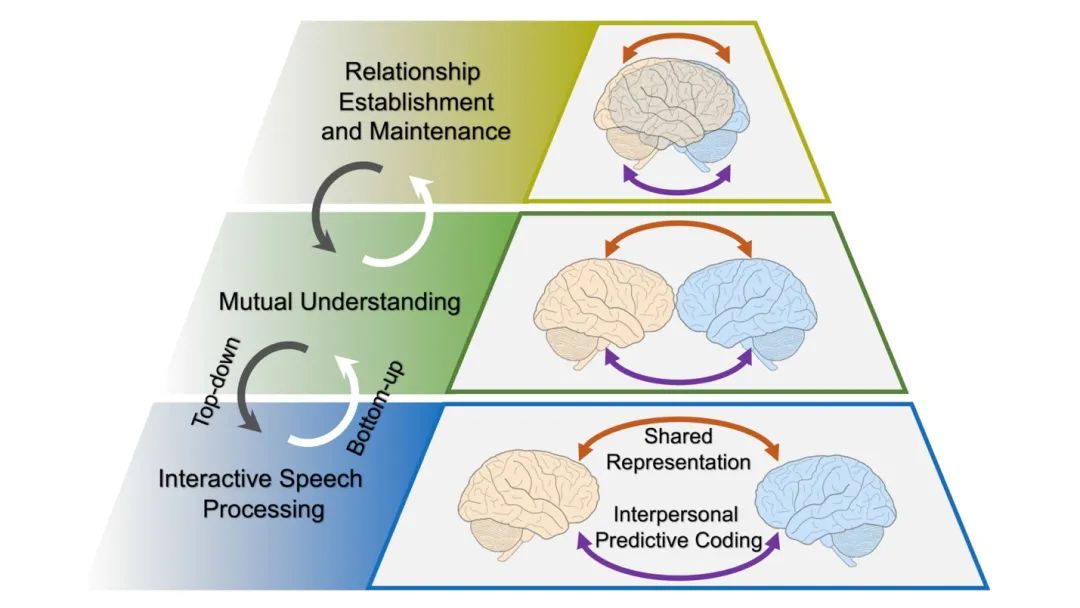
图1人际间言语交流的认知神经层级模型
该模型的核心观点包括:
该模型的核心观点得到了该课题组过去10年工作的支持,同时也与国际同行的相关研究结果相切合。模型为从交流的角度深入理解语言与人脑和人类智能的关系提供了重要的参考框架。作为国际上最早通过超扫描技术开展社会交流与互动研究的课题组之一,近年来,卢春明课题组建立并拓展了基于近红外光谱成像的超扫描方法体系,多角度深入探讨了自然情景下语言交流与社会互动的认知神经机制。课题组之前的多项研究工作发表在Nature Communication, PNAS, Journal of Neuroscience, Cerebral Cortex等国际权威期刊。
文章第一作者蒋静博士是卢春明课题组的第一位硕士(2010-2013),在德国马普人类认知与神经科学研究所及柏林洪堡大学取得博士学位(2013-2017),并先后在美国斯坦福大学和哈佛医学院从事博士后工作(2017-现在)。蒋静博士的长期研究目标是采用多模态行为和脑成像技术,如近红外超扫描(fNIRS-based hyperscanning),同步眼动/磁共振( concurrent eye-tracking/fMRI), 同步经颅磁刺激/磁共振( concurrent TMS/fMRI) 等,考察正常人和病人在社会性和情绪方面的认知神经机制。其研究工作主要发表在Nature Biotechnology, PNAS, Neuropsychopharmacology, Journal of Neuroscience, SCAN等期刊上。蒋静博士今年还获得由美国脑与行为研究基金会(Brain & Behavior Research Foundation, BBRF)选拔并资助的NARSAD青年研究者奖,以支持其在接下来两年里在抑郁等情绪、社交障碍研究方向的工作。
论文的第二作者郑丽芬博士目前在北京师范大学教育学部开展博士后研究工作,主要研究兴趣是将认知神经科学与与教育科学交叉,开展有效教学的认知神经机制研究,相关成果以第一作者和封面论文形式发表于Human Brain Mapping、SCAN等期刊。该综述中的部分重要观点来自郑丽芬博士的博士论文。
该研究得到了国家自然科学基金(61977008,31622030)和万人计划青年拔尖人才项目的资助。
文章连接:
卢春明课题组网站:
蒋静博士个人网站:
卢春明课题组相关文章列表:
1. Jiang J, Zheng L, Lu C (2020) A Hierarchical Model For Interpersonal Verbal Communication. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience.
2. Long Y, Zheng L, Zhao H, Zhou S, Zhai Y, Lu C (2020) Interpersonal Neural Synchronization during Interpersonal Touch Underlies Affiliative Pair Bonding between Romantic Couples. Cereb Cortex.
3. Zheng L, Liu W, Long Y, Zhai Y, Zhao H, Bai X, Zhou S, Li K, Zhang H, Liu L, Guo T, Ding G, Lu C (2020) Affiliative bonding between teachers and students through interpersonal synchronisation in brain activity. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience 15:97-109.
4. Liu L, Zhang Y, Zhou Q, Garrett DD, Lu C, Chen A, Qiu J, Ding G (2020) Auditory-Articulatory Neural Alignment between Listener and Speaker during Verbal Communication. Cereb Cortex 30:942-951.
5. Liu W, Branigan HP, Zheng L, Long Y, Bai X, Li K, Zhao H, Zhou S, Pickering MJ, Lu C (2019) Shared neural representations of syntax during online dyadic communication. NeuroImage 198:63-72.
6. Zheng L, Chen C, Liu W, Long Y, Zhao H, Bai X, Zhang Z, Han Z, Liu L, Guo T, Chen B, Ding G, Lu C (2018) Enhancement of teaching outcome through neural prediction of the students' knowledge state. Human brain mapping 39:3046-3057.
7. Dai B, Chen C, Long Y, Zheng L, Zhao H, Bai X, Liu W, Zhang Y, Liu L, Guo T, Ding G, Lu C (2018) Neural mechanisms for selectively tuning in to the target speaker in a naturalistic noisy situation. Nature communications 9:2405.
8. Jiang J, Chen C, Dai B, Shi G, Ding G, Liu L, Lu C (2015) Leader emergence through interpersonal neural synchronization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 112:4274-4279.
9. Jiang J, Dai B, Peng D, Zhu C, Liu L, Lu C (2012) Neural synchronization during face-to-face communication. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 32:16064-16069.

发表评论